Hello friends, today we are going to talk about- What is Liability Car Insurance? Definition, Scope, and Example. Liability auto insurance, an integral facet of car insurance policies, shields drivers financially in cases where their vehicular operation causes harm to others or their property.
It exclusively encompasses injuries or damages inflicted upon third parties and their belongings, excluding coverage for the driver or their possessions, which might be independently insured under other policy sections.
The dual components of liability auto insurance encompass bodily injury liability and property damage liability. Except for New Hampshire, all states mandate some level of liability coverage for drivers.
Key Highlights: Liability auto insurance acts as a financial safeguard for drivers involved in accidents that cause harm to others or property. Bodily injury liability aids in covering medical expenses for those impacted by the accident. Property damage liability contributes to the costs associated with repairing other drivers' vehicles involved in the accident.
Deciphering Liability Auto Insurance
Liability auto insurance plays a pivotal role in offsetting damages resulting from car accidents. Many states, if a driver is deemed at fault, their insurance provider shoulders the property and medical expenses of other involved parties, up to the predetermined policy limits.
In jurisdictions with no-fault auto insurance systems, irrespective of fault, drivers in accidents must initially file claims with their insurers. In these states, obtaining personal injury protection (PIP) coverage is typically mandatory, covering the driver’s accident-related medical expenses and those of their passengers.
Also Read: The Power of Forex VPS Hosting: Accelerating Your Trading Success
Liability auto insurance is bifurcated into two coverage types
- Bodily Injury: The bodily injury liability segment of a car insurance policy shields an at-fault driver from liability for emergency and ongoing medical expenses, loss of income, or funeral costs incurred by others. Additionally, it assists in covering the policyholder’s legal fees in the event of a lawsuit stemming from the accident.
- Property Damage: Property damage liability aids in covering the expenses related to repairing or replacing other drivers’ vehicles involved in the accident. It extends to damage inflicted on other forms of property by the policyholder’s vehicle, including fencing, mailboxes, or buildings.
Coverage Limits for Liability Auto Insurance
Liability auto insurance imposes monetary limits on each of its components, contingent on the chosen coverage level at the time of policy acquisition. These comprise:
- Liability Limit for Property Damage: The maximum coverage amount for property damage. Any costs surpassing this limit become the responsibility of the at-fault driver.
- Liability Limit for Bodily Injury per Person: The maximum sum the insurance company will disburse for each individual injured in an accident.
- Liability Limit for Bodily Injury per Accident: A financial ceiling for the total amount the insurance company will pay for all individuals involved in an accident. The at-fault driver assumes liability for any medical expenses exceeding this limit.
Note: Bodily injury liability coverage can safeguard one’s home and assets if facing legal action from a driver or passenger following an accident.
Mandatory Requirements for Liability Auto Insurance:
Each state stipulates a minimum level of liability coverage that motorists must carry. For instance, a state might mandate liability insurance covering $25,000 for one person’s injuries, $50,000 for injuries to multiple individuals, $50,000 for one person’s death, and $10,000 for property damage.
Motorists can typically opt for coverage exceeding their state’s minimums, a prudent choice given the potential exorbitance of medical bills.
For those with substantial assets vulnerable to potential lawsuits, acquiring an umbrella insurance policy is advisable. Such a policy can elevate liability coverage on both auto and homeowners insurance to $1 million or more.
Gap insurance is another consideration, particularly for owners of high-value vehicles prone to rapid depreciation.
Also Read: How can you reduce your total loan cost?
Illustrative Scenario of Liability Auto Insurance
Consider a scenario in a state without no-fault insurance. Assume the motorist holds the following liability auto coverage:
- Bodily injury liability limit per person: $60,000
- Bodily injury limit per accident: $150,000
In an accident involving multiple individuals, the at-fault driver is liable for damages. Medical costs are as follows:
- Person A: $30,000
- Person B: $40,000
- Person C: $50,000
The at-fault driver’s liability is covered, as each person’s medical expenses are below $60,000. The total costs for all involved parties (excluding the at-fault driver) amount to $120,000, below the per-accident bodily injury limit.
It’s crucial to recognize that some policies may not cover expenses exceeding the per-accident limit, even if per-person limits are not breached.
Using the aforementioned example, if each person had medical expenses of $55,000, despite falling within the per-person limit of $60,000, the total cost of $165,000 exceeds the per-accident limit of $150,000. Consequently, the at-fault driver assumes liability for the additional $15,000.
While states establish minimums for car insurance liability coverage, opting for coverage beyond the minimum is often a judicious decision.
Liability vs. Full-Coverage Automotive Insurance
In addition to mandatory liability coverage, insurers extend options like collision and comprehensive insurance. A policy encompassing all three—liability, collision, and comprehensive—is colloquially termed “full coverage.”
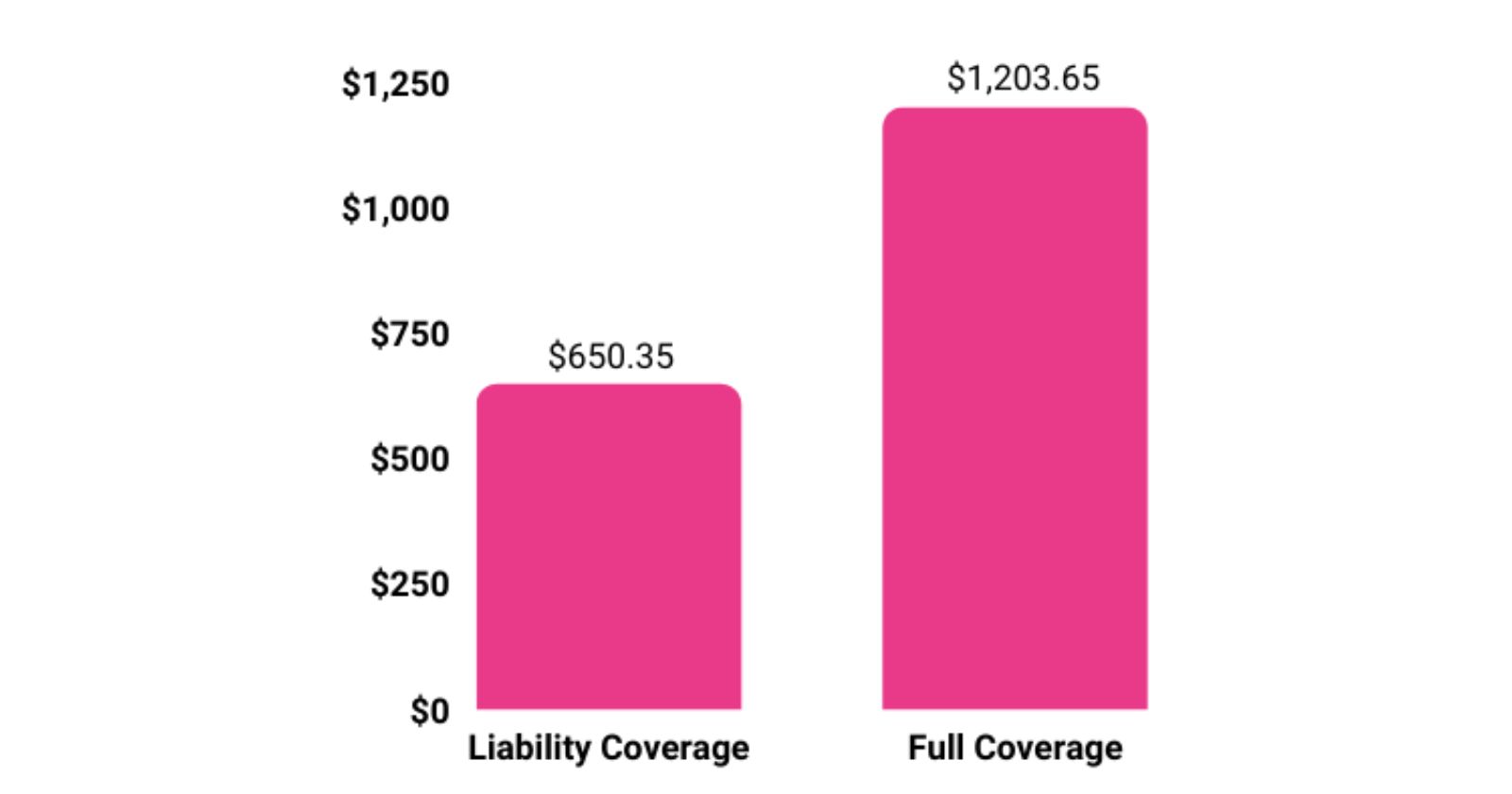
Although a full-coverage policy entails higher costs compared to liability-only policies, it provides broader protection against diverse financial risks.
Unlike property damage liability insurance, which covers damage to another person’s car, collision and comprehensive insurance safeguard the policyholder’s vehicle.
- Collision Insurance: Assists in repairing or replacing the policyholder’s car damaged in accidents involving other vehicles or objects like trees or walls.
- Comprehensive Insurance: Aids in replacing or repairing the insured vehicle if stolen or damaged in incidents beyond collisions. Comprehensive coverage typically includes damage from fire, vandalism, or non-collision events such as falling objects, large tree limbs, or hail.
These optional insurances are often required by lenders for financed vehicles to preserve the vehicle’s value as collateral. Even if not mandated, purchasing them is advisable unless one can easily cover significant repair costs out of pocket.
Given the potential variations in provisions from state to state, consulting an informed insurance agent familiar with state regulations is prudent. Additionally, comparing car insurance rates ensures securing the most advantageous coverage._
Conclusion
Exploring the intricacies of liability car insurance unveils a crucial layer of financial protection for drivers navigating the unpredictable roads of life.
From the shield provided by bodily injury and property damage liability to the critical understanding of policy limits, this journey through the realms of auto insurance aims to empower individuals with knowledge.
As the landscape of auto insurance evolves, conversations surrounding trending hashtags like #InsuranceInsights, #SmartInsuranceChoices, and #FullCoverageDeconstructed provide a dynamic platform for individuals to stay informed and engage in discussions that shape their insurance decisions.
In the grand scheme, liability auto insurance acts as a steadfast guardian against the financial aftermath of accidents, ensuring that drivers are not only protected but also equipped to make informed choices in safeguarding their assets and well-being.
As we navigate the ever-changing terrain of the insurance landscape, knowledge remains the key to unlocking a secure and well-informed journey on the roads ahead.


This site is fabulous. The radiant material shows the publisher’s enthusiasm. I’m dumbfounded and envision more such mind blowing substance.